We Should Know About Types Of Machine Learning
In This Article we will discuss more about Types Of Machine Learning.
Types Of Machine Learning :
As we know there is three types of Machine Learning.
- Supervised
- Unsupervised
- Reinforcement
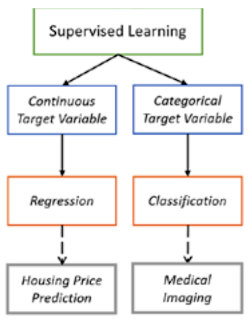
(1) Supervised :
- In Supervised Learning machine learns under guidance as a teacher guides the student.
- Machines learns from provided data to them and explicitly telling them this is the input and this is how the output must look.
- Here, the system is trained using past data(which includes input and output), and is able to take decisions or make predictions, when new data is encountered.
- In example of teacher and student teacher is training data and student is machine.
(2) Unsupervised :
- The system is able to recognize patterns, similarities and anomalies, taking into consideration only the input data.
- Unsupervised means without any supervision or without anybody's direction.
- Here the data is not labeled and there is no guide.
- Here, the system is trained using past data(which includes input and output), and is able to take decisions or make predictions, when new data is encountered.
- Unsupervised means without any supervision or without anybody's direction.
Recommended Articles :
- Machine has to figured out data set given and find out hidden patterns.
- In short machine has to make predictions.
- We can say Unsupervised learning is our daily activities on which we take decision own self.
(3) Reinforcement :
- Decisions are made by the system on the basis of the reward/ punishment it received for the last action it performed
- Reinforcement Learning means Machine takes decision once and gives output.if it's right then OK.
- Otherwise it gives feedback after that it data Re-train again.
- This process occurs till the output not comes right.
- so, basically this type learn from feedback and past experiences.
- Reinforcement Learning means Machine takes decision once and gives output.if it's right then OK.
In short terms :
1) Supervised :
- Labeled Data
- Direct Feedback
- Predict Outcome / Future
2) Unsupervised :
- No Labels
- No Feedback
- Find Hidden Structure In Data
3) Reinforcement :
- Labeled Data
- Direct Feedback
- Predict Outcome / Future
- No Labels
- No Feedback
- Find Hidden Structure In Data
3) Reinforcement :
Supervised
1) Classification
The data needs to be divided into a number of different categories based on training using past data.
An example of a classification problem, would be how we are able to sort emails are spam or otherwise using previously received emails that have been already identified.
A famous algorithm that can be used to solve classification problems, is the Naive Bayes theorem New Mail Classification Not Not spam Senator on spam Regression Learns Spam Spam Enables the machine to be trained to classify observations into some class
The data needs to be divided into a number of different categories based on training using past data.
An example of a classification problem, would be how we are able to sort emails are spam or otherwise using previously received emails that have been already identified.
A famous algorithm that can be used to solve classification problems, is the Naive Bayes theorem New Mail Classification Not Not spam Senator on spam Regression Learns Spam Spam Enables the machine to be trained to classify observations into some class
2) Regression
We predict a value for an input based on previously received information.
Although this sounds similar to classification considering that they both use past data to make predictions, their similarity ends there of regression,
you're trying to In the case estimate a value and not just a class of an observation Now let's consider weather prediction.
The likelihood of it raining today can be calculated by taking weather factors like temperature, humidity a measurement of other pressure, wind-speed, wind-direction and then seeing how they correlate to rains in the past.
If the measurements taken today are strongly correlated to days when it rained then the likelihood of it raining is high today The linear regression algorithm is one that's commonly used to solve this problem.
You May Also Like This Article :
We predict a value for an input based on previously received information.
Although this sounds similar to classification considering that they both use past data to make predictions, their similarity ends there of regression,
you're trying to In the case estimate a value and not just a class of an observation Now let's consider weather prediction.
The likelihood of it raining today can be calculated by taking weather factors like temperature, humidity a measurement of other pressure, wind-speed, wind-direction and then seeing how they correlate to rains in the past.
If the measurements taken today are strongly correlated to days when it rained then the likelihood of it raining is high today The linear regression algorithm is one that's commonly used to solve this problem.
You May Also Like This Article :
Unsupervised
1) Clustering
This uses a method where we assign a set of observations into subsets. These subsets are known as clusters.
The observations inside these clusters are similar to one another, based on some parameter or other Hence, all the data is divided into clusters.
An example of when clustering is used, when a telecom provider wants to set up a network in a region by setting up towers there,
They use the clustering algorithm, taking into consideration areas that would provide optimum connectivity to all users and the maximum range a cell tower would have, to divide the entire region into clusters.
K Means is a prominently used method to cluster data in k-clusters based on some similarity measures.
This uses a method where we assign a set of observations into subsets. These subsets are known as clusters.
The observations inside these clusters are similar to one another, based on some parameter or other Hence, all the data is divided into clusters.
An example of when clustering is used, when a telecom provider wants to set up a network in a region by setting up towers there,
They use the clustering algorithm, taking into consideration areas that would provide optimum connectivity to all users and the maximum range a cell tower would have, to divide the entire region into clusters.
K Means is a prominently used method to cluster data in k-clusters based on some similarity measures.
2) Association
In an association problem, we identify patterns of associations between different variables or items.
Its concepts are applied to e-commerce websites, where they're able to suggest other items for you to buy.
It is based on the prior purchases that you've done Previous shopping history Suggests Clustering Association Learns Flip-kart, amazon Identifies patterns of association between different variables and items
I hope this article is help to you for learn types of machine learning.
You can also learn :
In an association problem, we identify patterns of associations between different variables or items.
Its concepts are applied to e-commerce websites, where they're able to suggest other items for you to buy.
It is based on the prior purchases that you've done Previous shopping history Suggests Clustering Association Learns Flip-kart, amazon Identifies patterns of association between different variables and items
I hope this article is help to you for learn types of machine learning.
You can also learn :
Things You Should Know About Python Before Learning Python :
Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Developed by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991,
Python is an interpreted, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Developed by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991,
The Reasons For Why Writing Software Applications in Python
1) Readable and Maintainable Code
2) Multiple Programming Paradigms
3) Compatible with Major Platforms and Systems
4) Robust Standard Library
5) Many Open Source Frameworks and Tools
6) Simplify Complex Software Development
7) Adopt Test Driven Development
1) Readable and Maintainable Code
2) Multiple Programming Paradigms
3) Compatible with Major Platforms and Systems
4) Robust Standard Library
5) Many Open Source Frameworks and Tools
6) Simplify Complex Software Development
7) Adopt Test Driven Development
The Python Applications :
1) Web and Internet Development
2) Applications of Python Programming in Desktop GUI
3) Science and Numeric Applications
4) Software Development Application
5) Python Applications in Education
6) Python Applications in Business
7) Database Access
8) Network Programming
9) Games and 3D Graphics
10) Console-based Applications
11) Audio – or Video- based Applications
12) Applications for Images
13) Enterprise Applications
14) 3D CAD Applications
15) Computer Vision
16) Machine Learning
17) Robotics
18) Web Scraping
19) Scripting
20) Artificial Intelligence
21) Data Analysis
1) Web and Internet Development
2) Applications of Python Programming in Desktop GUI
3) Science and Numeric Applications
4) Software Development Application
5) Python Applications in Education
6) Python Applications in Business
7) Database Access
8) Network Programming
9) Games and 3D Graphics
10) Console-based Applications
11) Audio – or Video- based Applications
12) Applications for Images
13) Enterprise Applications
14) 3D CAD Applications
15) Computer Vision
16) Machine Learning
17) Robotics
18) Web Scraping
19) Scripting
20) Artificial Intelligence
21) Data Analysis
You Also Can Search For Other Python Keywords Like :
Python , Python For Loop , Python Loops , Python Tutor , Python Tutorial , Python Dictionary , Python Learning , For Python List , Python List , Python Anaconda , Python Download , Python Range , Python Regex , Python Else If , Python If Else , Python Programming , Python Snake , Python Class , Python Set , Python In Function , Python Function , Python 3 , Python Pandas , Python Random , Python Array , Python Requests , Python Tuple , Python Enumerate , Python Write To File , Python IDE , Python Logger
Python String , Python While Loop , Python Map , Python Install , Python Read File , Python Code , Python Flask , Python Json , Python Operator , Python Or Operator , Python Zip , Python Compiler Online , Python Online Compiler , Python Online , Python Replace , Python Join , Python Unit Testing , Python Unittest , Python Machine Learning , Python With Machine Learning , Python Certification , Why Python For Machine Learning , Python Interview Questions , Python gui , Python Reverse String , Python Compiler
The Python Regular Expression , Python Queue , Python 2.7 , Python Yield , Python Web Scraping , Python IDE Online , Python Django , Python Scripting , Python Numpy , Python Multithreading , For Python , Python Or , Python Generator , Python For Windows , Python 3.7 , With Python , Python Documentation , Python Version , Python Beginners , Python For Beginners , Python Language , Python List Functions , Python Projects , Python Data Structures , Python Mysql , Python Library , Python And , Python w3schools , Python Modules , Python Hello World , Python Data Types , Python 3.6 , Python Interpreter
Python Keyerror , Python Ord , Python Meaning , Python Ordereddict , Python Xrange , Pythonanywhere , Python Range Function , Python For Data Analysis , Python With Data sScience , Python For Data Science , Python Basics , Python Interpreter Online , Python Online interpreter , Python Cheat Sheet , Python Cheat Sheet , Python vs Java , Python Syntax , Python Xml Parser , Python Xml Parsing , Python Join List , Python Editor
Python , Python For Loop , Python Loops , Python Tutor , Python Tutorial , Python Dictionary , Python Learning , For Python List , Python List , Python Anaconda , Python Download , Python Range , Python Regex , Python Else If , Python If Else , Python Programming , Python Snake , Python Class , Python Set , Python In Function , Python Function , Python 3 , Python Pandas , Python Random , Python Array , Python Requests , Python Tuple , Python Enumerate , Python Write To File , Python IDE , Python Logger
Python String , Python While Loop , Python Map , Python Install , Python Read File , Python Code , Python Flask , Python Json , Python Operator , Python Or Operator , Python Zip , Python Compiler Online , Python Online Compiler , Python Online , Python Replace , Python Join , Python Unit Testing , Python Unittest , Python Machine Learning , Python With Machine Learning , Python Certification , Why Python For Machine Learning , Python Interview Questions , Python gui , Python Reverse String , Python Compiler
The Python Regular Expression , Python Queue , Python 2.7 , Python Yield , Python Web Scraping , Python IDE Online , Python Django , Python Scripting , Python Numpy , Python Multithreading , For Python , Python Or , Python Generator , Python For Windows , Python 3.7 , With Python , Python Documentation , Python Version , Python Beginners , Python For Beginners , Python Language , Python List Functions , Python Projects , Python Data Structures , Python Mysql , Python Library , Python And , Python w3schools , Python Modules , Python Hello World , Python Data Types , Python 3.6 , Python Interpreter
Python Keyerror , Python Ord , Python Meaning , Python Ordereddict , Python Xrange , Pythonanywhere , Python Range Function , Python For Data Analysis , Python With Data sScience , Python For Data Science , Python Basics , Python Interpreter Online , Python Online interpreter , Python Cheat Sheet , Python Cheat Sheet , Python vs Java , Python Syntax , Python Xml Parser , Python Xml Parsing , Python Join List , Python Editor